The Commonwealth is one of the world’s oldest political associations of states. Its roots go back to the British Empire, when countries around the world were ruled by Britain.
The early Commonwealth
Over time different countries of the British Empire gained different levels of freedom from Britain. Semi-independent countries were called Dominions. Leaders of the Dominions attended conferences with Britain from 1887.
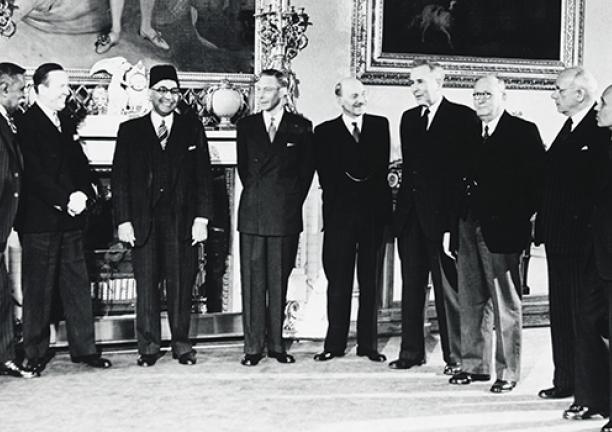
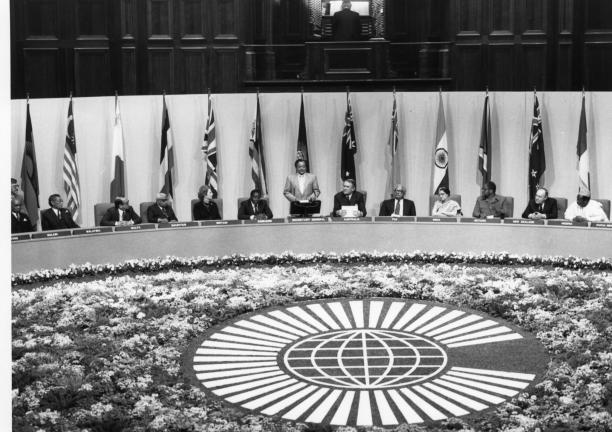
The 1926 Imperial Conference was attended by the leaders of Australia, Canada, India, the Irish Free State, Newfoundland, New Zealand and South Africa.
At the 1926 conference Britain and the Dominions agreed that they were all equal members of a community within the British Empire. They all owed allegiance to the British king or queen, but the United Kingdom did not rule over them. This community was called the British Commonwealth of Nations or just the Commonwealth.
Birth of the modern Commonwealth
The Dominions and other territories of the British Empire gradually became fully independent of the United Kingdom.
India became independent in 1947. India wanted to become a republic which didn't owe allegiance to the British king or queen, but it also wanted to stay a member of the Commonwealth.
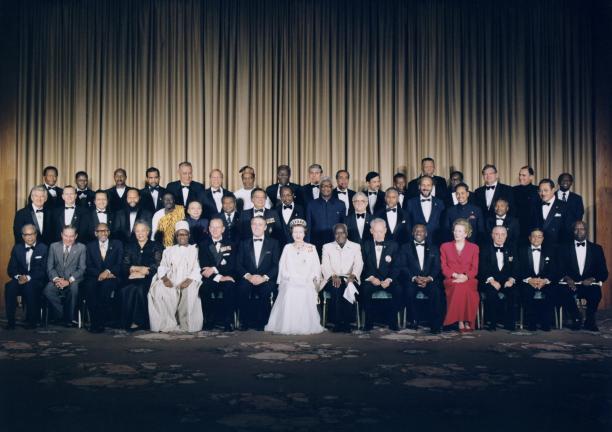
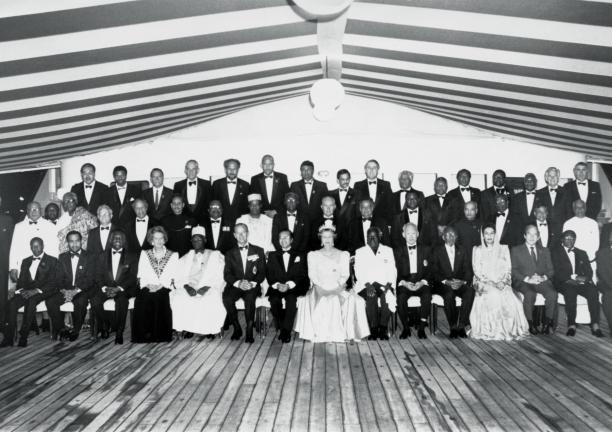
At a Commonwealth Prime Ministers meeting in London in 1949, the London Declaration said that republics and other countries could be part of the Commonwealth. The modern Commonwealth of Nations was born.
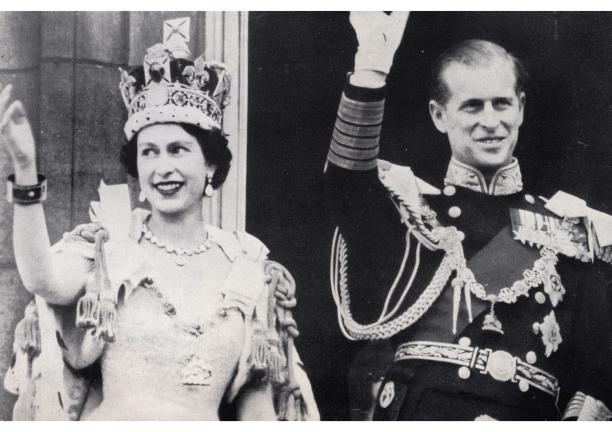
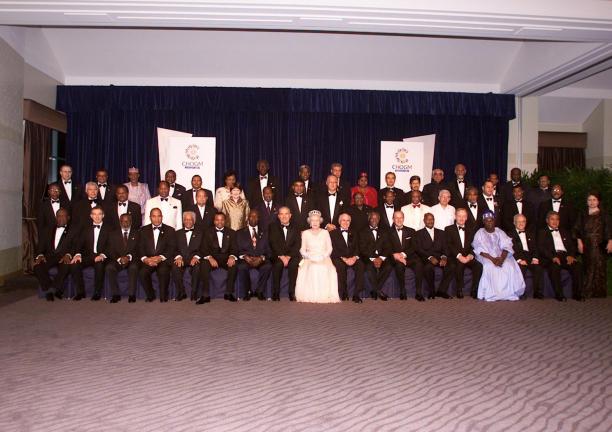
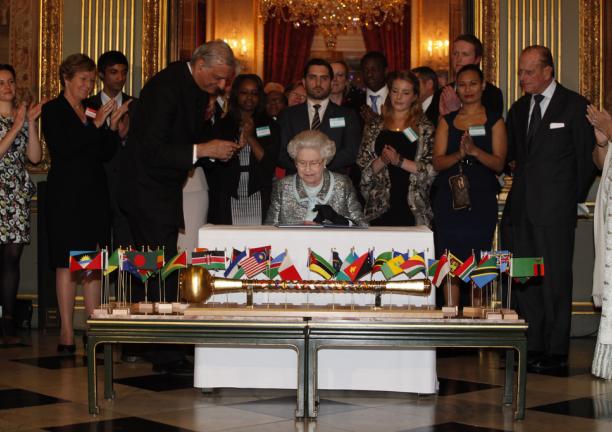
King George VI was the first Head of the Commonwealth, and Queen Elizabeth II became Head when he died. But the British king or queen is not automatically Head of the Commonwealth. Commonwealth member countries choose who becomes Head of the Commonwealth.
Speaking on this new association in 1953 Her Majesty the Queen said: “Thus formed, the Commonwealth bears no resemblance to the Empires of the past. It is an entirely new conception, built on the highest qualities of the spirit of man: friendship, loyalty and the desire for freedom and peace. To that new conception of an equal partnership of nations and races I shall give myself heart and soul every day of my life.”
The modern Commonwealth
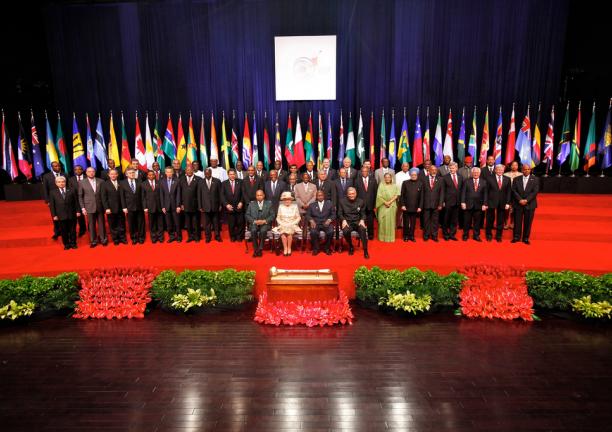
Since 1949 independent countries from Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe and the Pacific have joined the Commonwealth. Membership today is based on free and equal voluntary co-operation.
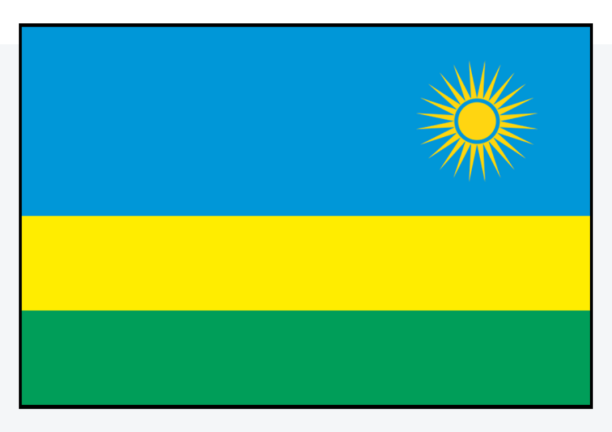
The last four countries to join the Commonwealth - Mozambique, Rwanda, Gabon and Togo - have no historical ties to the British Empire.
The Commonwealth Secretariat was created in 1965 as a central intergovernmental organisation to manage the Commonwealth's work.